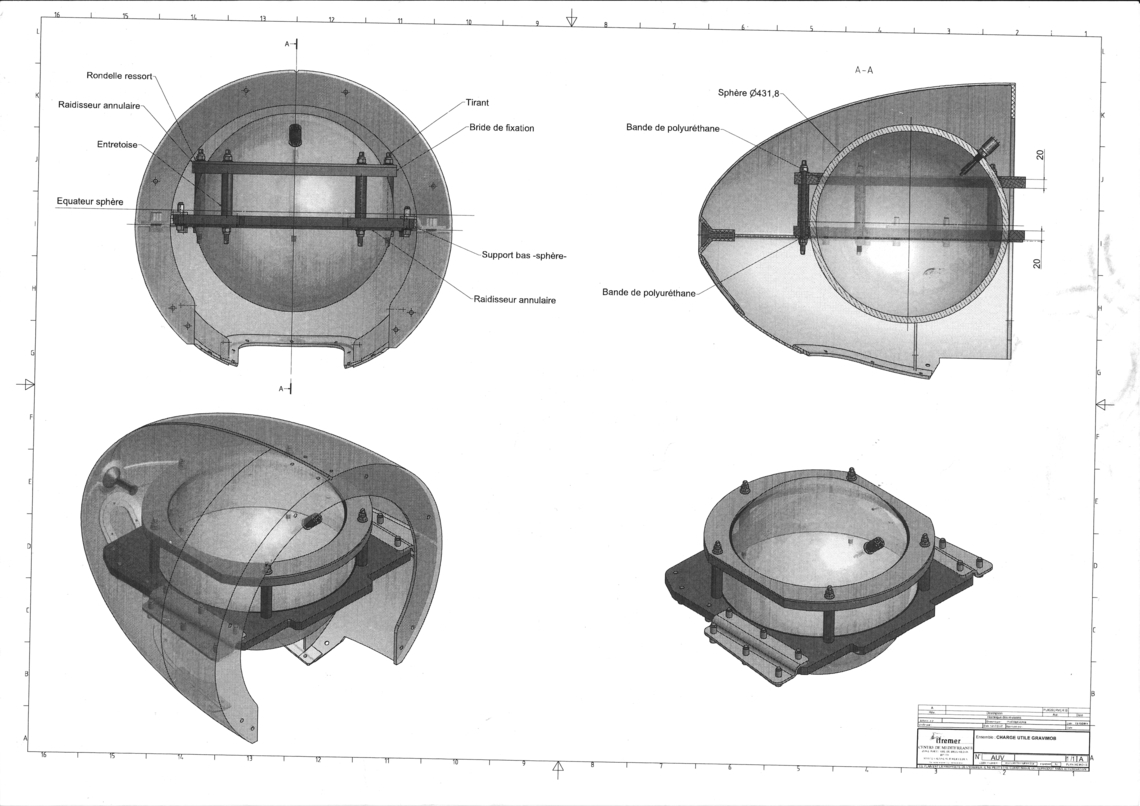
Gravimob
GRAVIMOB (Mobile Underwater Gravimeter) is an underwater instrument for measuring anomalies in the Earth's gravity field. It features a 17-inch-diameter hyperbaric sphere with no mobile mechanical parts and can be attached to any carrier vehicle with a 24V power socket.
Underwater gravimetric measurement technology is still in its early stages of development. The use of conventional instruments calls for a large, stable platform, and the payload of a small AUV is rapidly depleted.
The GRAVIMOB system is based on an innovative concept of the joint use of acceleration and attitude measurements of a vehicle to determine anomalies in the Earth’s gravity field.
Two test campaigns were carried out on the oceanographic vessel Europe in 2016 and 2021. The instrument is fitted into the nose of the AUV Aster'X or Idef'X. The data obtained allowed us to improve the algorithms for evaluating anomalies in the Earth's gravity field.
.
The GRAVIMOB project covers a wide range of application areas:
- Fundamental research :
- Regional geological mapping
- determination and improvement of the terrestrial geoid
- archaeological excavations
- sediment thickness measurements
- Exploitation of natural resources
- Oil and gas exploration
- mineral exploration
- Underwater navigation / Defence
- Gravimetric navigation charts (in addition to bathymetric charts)
- Drift correction of inertial units on submarines
GRAVIMOB is a collaborative project between the Laboratoire Géomatique et Foncier de l’ESGT - Le CNAM in Le Mans (Jérôme Verdun & José Cali) and Geo-Ocean in Plouzané (Marcia Maia, Jérôme Ammann, Charles Poitou, Dinh Toan Vu).
Project funders:
- Institut Carnot Mers (74500 euros)
- CPER - région Bretagne (106 000 euros)
- CNRS
- Labex Mer (ex-Isblue)
- L’europe (FEDER O3DO)